redshift-fake-driverでAmazon Redshiftをモックする
Amazon Redshiftは便利でコスパのよいDWHですが、時間に対する従量課金なので、ちょっとした動作確認のために立ち上げっぱなしにしとくのが気がひける場合もあります。
もしJVMプロジェクトを開発しているなら、redshift-fake-driverを使うことでRedshiftを代替できます。 github.com
What is redshift-fake-driver
Redshift固有のSQL syntaxを無視したり同等のものに置き換えてPostgresqlまたはH2にプロキシする、JDBCドライバーです。
UNLOAD, COPYのようなコマンドもサポートしています。
その場合、Java system propertyでS3エンドポイントを渡すことで、fake-s3のようなS3互換のモックを使うことも可能です。
Usage
では、fake-s3とPostgresqlを使って、使い方を見ていきます。
言語はScalaで、実行はAmmonite REPLで行います。
0. Postgresqlのセットアップ
$ createuser sample_user $ createdb -O sample_user sample_database
1. fake-s3のセットアップ
$ gem install fakes3 $ fakes3 -r ./fakes3_root -p 9444
2. 依存の追加
redshift-fake-driverは、artfifactにAWS SDKやPostgresql driverを含まないため、それらの依存を追加する必要があります。
以降、Ammonite REPLは立ち上げっぱなしと仮定します。
$ amm scala> import $ivy.`com.amazonaws:aws-java-sdk-s3:1.11.43` scala> import $ivy.`org.postgresql:postgresql:9.4.1211`
3. バケット作成
scala> import com.amazonaws.auth.BasicAWSCredentials
scala> import com.amazonaws.services.s3.{S3ClientOptions, AmazonS3Client}
scala> val options = S3ClientOptions.builder().setPathStyleAccess(true).build()
scala> val s3Client = new AmazonS3Client(new BasicAWSCredentials("DUMMY", "DUMMY"))
scala> s3Client.setEndpoint("http://localhost:9444/")
scala> s3Client.setS3ClientOptions(options)
scala> s3Client.createBucket("bar")
4. redshift-fake-driverのインストール
scala> import $ivy.`jp.ne.opt::redshift-fake-driver:1.0.7`
Scala以外のJVM言語の場合、artifact名はredshift-fake-driver_2.11などとすればよいです。
また今回fake-s3を使うため、Java system propertyを以下のように設定します。
scala> sys.props.put("fake.awsS3Endpoint", "http://localhost:9444/")
scala> sys.props.put("fake.awsS3Scheme", "s3://")
5. CREATE TABLE
Redshift固有の情報を含んだDDLでテーブルを作成します。
redshift-fake-driverを使うときは、JDBC接続文字列をjdbc:postgresqlredshiftで始めます。
scala> import java.util.Properties
scala> import java.sql._
scala> val url = "jdbc:postgresqlredshift://localhost:5432/sample_database"
scala> val prop = new Properties()
scala> prop.setProperty("driver", "jp.ne.opt.redshiftfake.postgres.FakePostgresqlDriver")
scala> prop.setProperty("user", "sample_user")
scala> Class.forName("jp.ne.opt.redshiftfake.postgres.FakePostgresqlDriver")
scala> val conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, prop)
scala> val stmt = conn.createStatement()
scala> stmt.execute("""
|CREATE TABLE foo_bar(a int ENCODE ZSTD, b varchar(255))
|DISTSTYLE ALL
|DISTKEY(a)
|INTERLEAVED SORTKEY(a, b);
|""".stripMargin)
ちゃんとテーブルが出来ています。
$ psql -U sample_user -d sample_database
sample_database=> \d foo_bar
Table "public.foo_bar"
Column | Type | Modifiers
--------+------------------------+-----------
a | integer |
b | character varying(255) |
6. UNLOAD
まずデータを入れます。
$ psql -U sample_user -d sample_database sample_database=> INSERT INTO foo_bar (a, b) VALUES (1, 'one'); sample_database=> INSERT INTO foo_bar (a, b) VALUES (2, 'two');
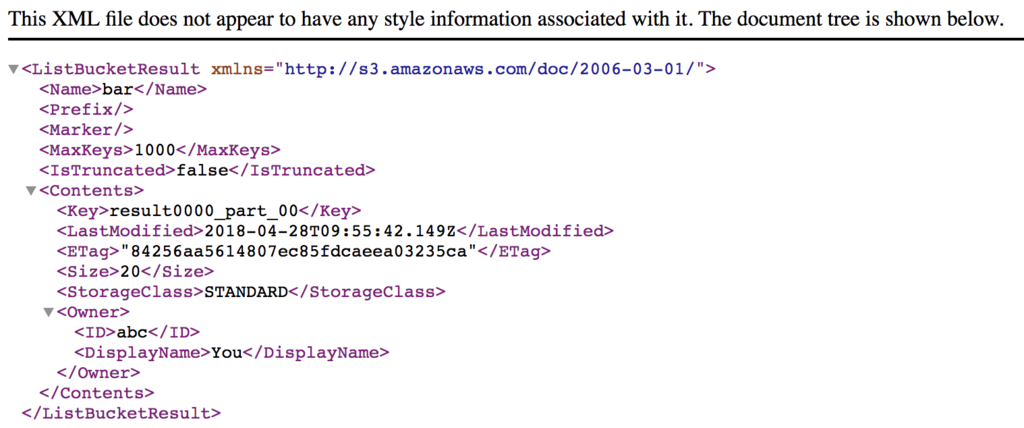
UNLOADを打って、fake-s3のデータを確認します。
scala> stmt.execute("""UNLOAD ('select * from foo_bar') to 's3://bar/result'
|CREDENTIALS 'aws_access_key_id=DUMMY;aws_secret_access_key=DUMMY'
|ADDQUOTES""".stripMargin)
ちゃんとデータが出来ていることがわかります。